
The Cheeky Monkey Media Blog
A few words from the apes, monkeys, and various primates that make up the Cheeky Monkey Super Squad.

The Importance of Maintenance and Being on a Maintenance Schedule: Key Strategies for Reliability and Efficiency
 April 4, 2024 / Ashley Olsen
April 4, 2024 / Ashley Olsen
Regular maintenance is an essential aspect of ensuring the longevity and optimal functioning of various systems, be it machinery, infrastructure, vehicles, or even personal health. Adhering to a maintenance schedule is key to maintaining efficiency, safety, and reliability. By proactively managing wear and tear, a structured maintenance routine helps avert minor issues from developing into major breakdowns, which can lead to expensive repairs, operational downtime, and sometimes irreversible damage.
Setting up a regular maintenance routine serves several critical functions. It helps prolong the lifespan of equipment, preserves the value of assets, and ensures that safety standards are consistently met. Whether it’s performing oil changes in a car, replacing filters in HVAC systems, or conducting regular checks on a production line, following a well-defined maintenance plan is crucial for continuous and smooth operation.
Neglecting regular maintenance can have serious repercussions, including elevated operational costs, unsafe working conditions, and a marked decrease in efficiency and productivity. Maintenance transcends being a mere technical requirement; it’s a strategic approach integral to the overall success and sustainability of a business, or the effective functioning of personal assets.
Understanding Maintenance and Scheduling
Effective maintenance is critical for the longevity and reliability of any system. Scheduling regular check-ups is indispensable for identifying issues before they escalate.
Benefits of Regular Maintenance
Reliability and Performance
Regular maintenance ensures that systems, especially web-based platforms, operate smoothly. It prevents downtime by identifying potential faults proactively. For example, website maintenance involves checking for broken links, outdated content, and ensuring that security patches are up to date, thereby maintaining site integrity and user trust.
Security
Regular web maintenance includes updating security features to protect against the latest threats. This guards sensitive data and maintains user confidence.
Cost Savings
Regular check-ups can save money in the long run by avoiding the high costs associated with emergency repairs, which often come at a premium.
Developing a Maintenance Schedule
Assessment and Planning
Creating an effective maintenance schedule starts with assessing the specific needs of the website or system. Factors to consider include the complexity of the web architecture, traffic patterns, and the criticality of the web presence for business operations.
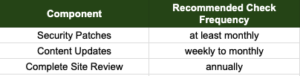
Frequency
Maintenance frequency depends on several factors, including:
- The size of the website
- User load and interaction levels
- The complexity of the website’s functionality
Documentation and Task Delegation
Documenting a maintenance schedule ensures clarity and consistency. In web management, teams should know who is responsible for each maintenance task, streamlining the process and minimizing the risk of oversight.
Consistency
Adherence to a regular schedule is paramount. It ensures all tasks are carried out without fail, maintaining the health of the system.
Executing and Managing Maintenance Tasks
Effective maintenance is critical for uninterrupted website operations and the facilitation of seamless WebOps. The following subsections outline the specific roles and streamlined processes that are essential to the robust management of intricate website systems.
Website Operations and Oversight
Website management requires persistent monitoring and quick resolution of issues. Administrators must ensure that all components, from the server hardware to the application software, are functioning optimally. A key strategy includes:
- Routine Inspections: Scheduled reviews keep systems up-to-date and secure. These inspections may cover:
- Server health checks: Assessing performance and capacity to prevent downtimes.
- Code audits: Looking for bugs or areas of improvement in website functionality.
WebOps: Streamlining Maintenance Processes
WebOps, or website operations, involves the application of streamlined maintenance procedures to enhance performance and reliability. They systematize recurring tasks such as updates, backups, and security checks, often utilizing automation tools. Incorporating WebOps effectively, one must:
- Automate: Deploy scripts or software that automate routine maintenance tasks.
- Monitor Continuously: Utilize tools that provide real-time alerts for any anomalies or performance degradation.
By applying these focused strategies, companies can ensure their websites are robust, secure, and perform at peak efficiency.